
VoIP means Voice over IP telephony or Voice Over Internet Protocol is a proven technology that allows people to make phone calls over an Internet connection rather than relying on physical landlines. Developed in 1995, it has turned into the go-to solution for more and more businesses when upgrading their phone systems.
This in-depth guide will walk you through all the essentials of VoIP technology and VoIP phone service.
Table of Contents
- What is VoIP? →
- How does VoIP work? →
- VoIP service vs. Landlines →
- Pros and Cons of VoIP →
- What is a VoIP phone? →
- Best VoIP phone system features →
- How much does VoIP cost?
- Do I need to upgrade from analog to VoIP? →
- How to choose a VoIP Provider →
- VoIP Phone System Buyer’s Guide →
- Technical VoIP Terminology →
- History of VoIP →
VoIP Phone System with Easy-first Unified Communications
Trusted by over 450,000 users, Yeastar PBX phone systems enable seamless IP telephony and include other essential enterprise-level functionality at small business costs: easy user apps, advanced contact center features, video conferencing, integration with WhatsApp, SMS, Microsoft Teams, CRMs and more. The solution offers 30-day free trial and there is no commitment to get started.
What is VoIP (Voice Over IP)?
VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) is a technology that allows users to make voice and multimedia calls over the internet instead of landline services. It converts voice data into digital packets, compresses it, and sends it over the internet, allowing users to make calls from various devices such as computers, smartphones, and special VoIP phones. Some may also refer to VoIP as Voice over IP, IP telephony, Internet telephony, broadband telephony, or broadband phone service.
This technology is widely used in business phone systems and personal VoIP applications like Skype and WhatsApp. Phone providers leverage VoIP technology to deliver telephone services to customers, eliminating the need for customers to install and maintain physical phone lines and equipment. VoIP enables high-quality calls and provides advanced features not typically available on traditional landline services, enhancing the overall communication experience.
Here is a short video to help you understand VoIP is in a minute:
How Does VoIP Work?
As mentioned above, VoIP works by converting voice audio into digital data packets and transmitting them over the Internet. The data packets travel between your phone and a VoIP provider (like your Internet Telephony Service Provider) to set up a call. This process involves several key steps:
- Your phone connects to your switch or router with your Local Area Network (LAN).
- When you dial a phone number, your phone tells your VoIP service provider to call the other party.
- The provider establishes the call and exchanges data packets from your phone.
- Your VoIP phone converts these digital signals into the sound you can hear.
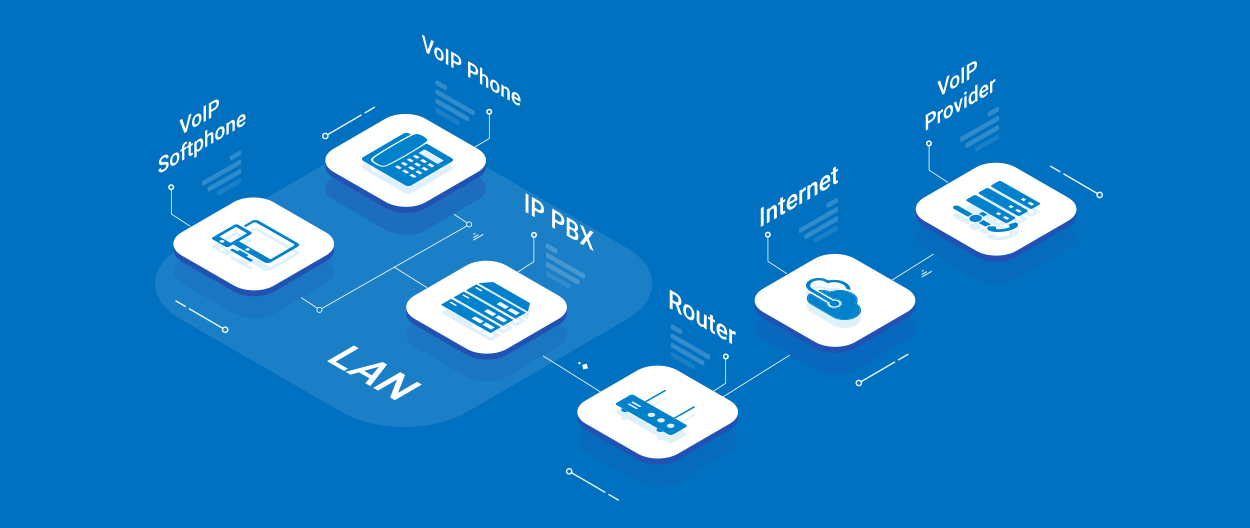
Equipment You May Need to Set up VoIP
- VoIP phone systems (PBX)
A VoIP PBX (Private Branch Exchange) is a business telephone system that facilitates phone calls over the company’s LAN or WAN data network rather than through the circuit-switched networks. It’s available in two deployment options – on-premises and cloud-based. With an on-premises voice solution, the hardware is installed and runs on-site at your office or data center while a cloud PBX system is delivered entirely over the Internet and managed completely off-site by a service provider. - VoIP phones or IP phones
VoIP phones, or IP phones, are the physical office phones that you can use with a VoIP phone system. They resemble traditional phones but are internet-enabled, connecting via WiFi or Ethernet. Each phone is assigned an IP address to facilitate calls over your network, making it easy for employees to adapt to the new technology. - Mobile phones, computers, network-ready devices
In addition to IP phones, VoIP systems can be accessed using mobile devices, computers, and other network-ready devices with VoIP apps or softphones. This allows employees to make and receive business calls from anywhere, using any device with an internet connection, without compromising call quality. - VoIP gateways
A VoIP gateway is a hardware device that converts traditional telephony traffic (analog or digital) into packets of data, allowing connections between legacy telephony infrastructure and IP-based communications, acting as a bridge between an IP network, the PSTN (Public Switched Telephone Network), and the cellular network.
What Is the Difference Between VoIP and Landline Phones?
Landline phones (or legacy analog phone systems) carry voice signals using analog phone lines (ISDN/PSTN) so it requires the setup of circuit wiring to make and receive calls. Under this circumstance, a piece of specialized hardware equipment called Private Branch Exchange (PBX) is used to connect internal phone extensions to the public telephone network.
On the other hand, Voice over IP telephony is a more modern technology that transmits data via your local area network/WAN/other infrastructure to enable phone calls. VoIP uses RTP (real-time protocol) to ensure that these packets get delivered timely. You can use either an ethernet cable or a high-speed WiFi connection for broadband telephony sevice.
Pros and Cons of Voice over IP?
Modern businesses enjoy using VoIP phone service over traditional telephone lines because they can get a lot more value than just improving corporate communications. Below are a few of the many ways VoIP benefits businesses.
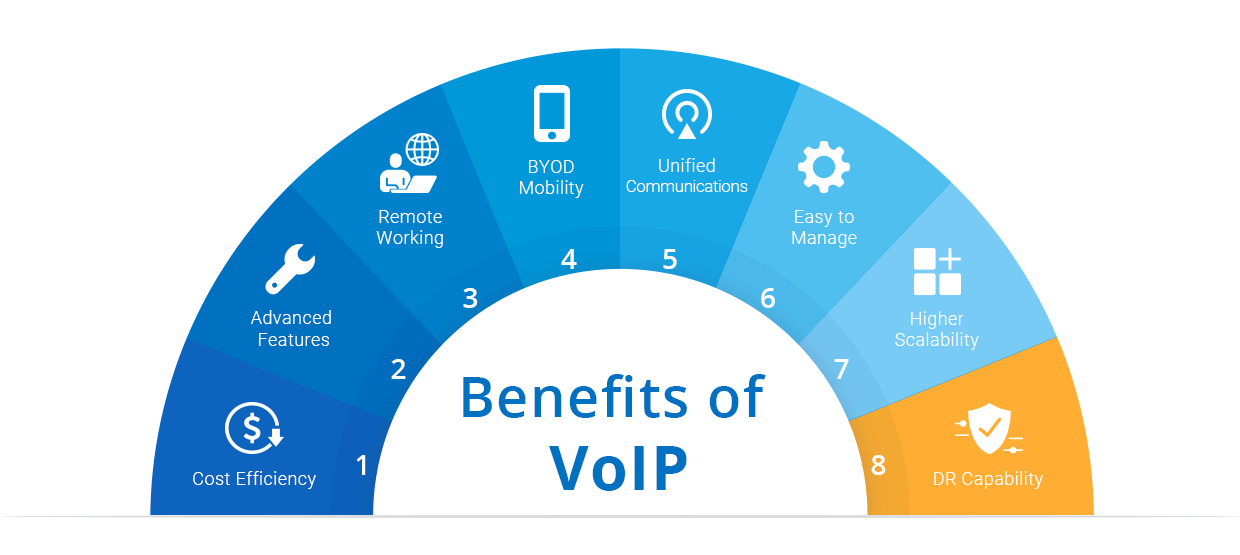
Advantages of VoIP
- Cost savings — Eliminates internal call costs, reduces external and international call expenses, and eliminates the need for traditional phone lines and maintenance. A VoIP phone system is also cheaper in the total cost of ownership when compared to a traditional analog phone system.
- Easy to install — No physical phone lines are required; IP phones simply connect to the corporate network via Ethernet lines. Additionally, if you are choosing hosted VoIP phone services, the service provider with take care of all the upkeep, making it a convenient option for small businesses and start-ups with limited technical expertise.
- Clear voice quality— With advancements in broadband and Voice over IP technology, VoIP call quality is now comparable to or even better than landline calls.
- Remote-friendly — Extend your communications system to remote offices and on-the-go workers over SIP-enabled devices. For remote workers, the office is wherever they make it as long as the Internet connection is available.
- Advanced features – Offers premium features like auto attendants, call recording, and call queues – without having businesses install expensive add-ons.
- Scalability — Cloud-based IP telephony services offer flexibility, allowing you to instantly add or remove phone extensions without purchasing new hardware or dedicated lines. This makes it ideal for businesses with fluctuating needs or rapid growth.
Disadvantages of VoIP
The only real downside of using Voice over Internet Protocol instead of a traditional phone system is that you rely on your internet connection for call quality. If you have a high-speed broadband connection, you should be fine. But it’s always best to check.
- Dependence on Internet Connection —Voice over IP requires a reliable and fast internet connection to function properly. Any disruptions or outages can cause call drops or poor call quality.
- Latency and Jitter — Calls can suffer from latency (delays) and jitter (variations in packet arrival times), which can affect call quality and make conversations difficult.
- Quality of Service (QoS) — Ensuring consistent call quality can be difficult, especially in networks that do not prioritize VoIP traffic. QoS settings need to be configured properly to maintain call quality.
What is a VoIP Phone?
A VoIP phone is a type of telephone that uses Voice Over IP technology to send and receive calls over an internet connection instead of traditional phone lines. Here are some key points about VoIP phones:
- Internet Connection: They connect to a network using Ethernet or Wi-Fi.
- Digital Conversion: They convert analog voice signals into digital data packets for transmission.
- Features: They often include features like voicemail, call forwarding, and call conferencing.
- Flexibility: Users can make calls from anywhere with an internet connection, enhancing mobility and flexibility.
VoIP phones can be physical devices that look similar to traditional phones or software-based virtual phones that operate on a computer or mobile device. They are widely used in businesses for their cost-effectiveness and advanced features.
Yeastar Softphone for easy call, meet, chat anywhere, on any devices
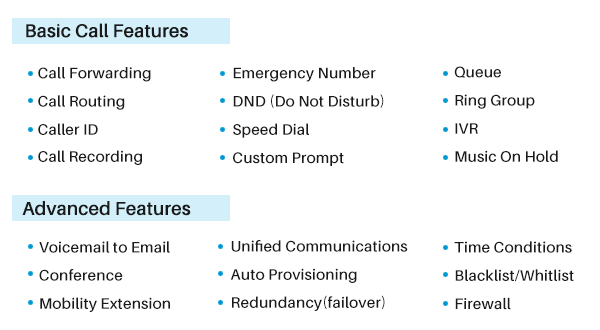
Best VoIP Phone System Features
What are the attractive features available with a cloud-based business phone system? Here are the most popular VoIP features that businesses will enjoy using.
-
Call Forwarding
When the called party is unavailable, Call Forwarding helps redirect incoming calls to another desired destination, such as the mobile phone number or other telephone numbers. You can also set up different rules for various scenarios. For example, route calls to another extension when you are busy, ring your mobile phone when no one answers calls to your desk phone, and ask callers to leave voice messages when you are on vacation.
-
Interactive Voice Response (IVR)
IVR or Auto Attendant helps even small businesses offer 24/7 customer services without costly human resources. When customers call in, pre-recorded greetings will direct them to the most appropriate destination with the minimum waiting time. With IVR, you can automate customer service and provide satisfactory answers timely.
-
Queue
It is a smart move to let an incoming call queue up while waiting for an available agent. Better than being on hold or going to voicemail, callers are informed of the estimated wait time. It reduces the number of missed calls as well as the negative effect of busy signals on customer experience. This feature is a must-have if you are running a call center.
-
Music on Hold
Phone calls may be put on hold sometimes, such as the intervals while you transfer a call to another number. Nobody likes awkward silences, so just upload some audio files and customize the on-hold music to please your customers and enhance your corporate image.
-
Call Recording
VoIP phone systems can be set up to automatically detect and record every phone conversation made over the system, including inbound and outbound calls. Businesses usually leverage call recordings for training, dispute resolution, compliance, and customer satisfaction tracking.
How Much Does VoIP Cost?
The cost of VoIP phone service varies depending on several factors, including the provider, number of users, and features. To give you an idea, here’s how much VoIP typically costs:
- Initial costs: $0-$50 per line
- Monthly costs: $19-$45 per line
- Device costs: $80-$600 per IP phone
- International calls: $0.01+ per minute
- Taxes and fees: Varies based on your city, county, and state
- VoIP Phone System costs: Varies based on the providers and supported features
Do I need to upgrade from landline to VoIP?
If you’ve been using traditional phone systems for a long time, it’s understandable to have doubts about transitioning to VoIP. To make an informed decision, consider the following questions:
1) Is your country experiencing the ISDN switch-off?
As technology advances and demands on business communications grow rapidly, the traditional PSTN and ISDN lines can barely live up to the expectations of today’s businesses, gradually slipping further and further into obsolescence. Now the ISDN switch-off is happening all around the globe. As large telecom companies successively announce to switch off ISDN and PSTN, Germany, Australia, Italy, and many other countries around the globe are experiencing a transformation from traditional landlines to all IP solutions.
If you are among the trend, it is critical f to find a seamless and reliable VoIP solution in response to the shutdown. Otherwise, you could lose your telephone service. If you aren’t facing an immediate ISDN switch-off, pay attention to this issue as you may find that your nation mandates this in the future. You can get ahead of future developments by planning to implement VoIP technology sooner rather than later.
2) Do you have employees working from home?
Since the outbreak of COVID-19, many businesses, which used to be restricted to traditional landlines, have upgraded to Cloud phone systems to facilitate a teleworking environment. Thanks to VoIP, the remote workforce can make and receive business calls with the same number they have in the office with their own devices and access the same calling capabilities.
Internet-based telephony has become a must-have tool for remote working and also a major step towards digital transformation. Furthermore, by using a VPN (virtual private network) connection along with the VoIP solution, your conversation will be shielded by a tunnel of encryption. A reliable VoIP service provider should be able to provide detailed information on how they secure remote and long-distance communications for customers.
3) Can your current analog system address your needs?
There are several major problems plaguing traditional telephone services.
First of all, traditional PBXs require a high upfront investment, including the purchase of phone lines and hardware (which also needs to be installed by experienced technicians), as well as ongoing maintenance fees. After the installation, it can also be expensive and difficult to scale the system when you experience the need for expansion, such as a significant increase in staff or additional branch locations.
Besides, traditional telephone systems generally provide only basic call features and cannot cope with more sophisticated business communication scenarios. With an increasing number of mobile and remote workforce, lack of mobility is becoming one of its major drawbacks. Analog phone services rely on physical lines to transmit voice traffic, which chains employees at desks to handle business calls.
Unlike a modern option like VoIP, customization and integration are quite limited on legacy phone systems. They are not able to integrate into today’s business communications ecosystem, which consists of a complex series of advanced applications, leaving voice calls in soils from the rest of a business’s information systems.
Keep reading to find out more about whether a VoIP Phone system makes sense for your business.
Things to Consider When Choosing a VoIP Service
It could have a huge impact on your business when deciding on a business communications solution. IP telephony service may be the best solution, but it’s important to conduct a current state and needs analysis first. Then, you can determine if business VoIP works for you. Here are some tips to help you determine your needs and make smart choices.
1) Do you want to keep existing equipment? Does it support your needs?
If you are using the traditional PBX and with a limited budget for a complete replacement of the existing equipment, make sure you select a VoIP solution that allows you to take a phased transition. Whether the new IP-based phone system is compatible with your traditional phone system, how to connect them together, how to ensure that the upgrade does not affect business continuity, etc. It’s also important to verify that the VoIP service providers you are considering will support that equipment. This is a stage where direct communication with the VoIP provider is key.
2) What kind of unified communications capabilities does it offer?
VoIP phone systems offer a range of telephony functionalities to handle audio calls, but communication with colleagues and customers is not only limited to voice. This is why unified communications is introduced to the business communications landscape and also why UC should be one of the top priorities as you evaluate your VoIP options.
Unified communications at its simplest is all about making a wealth of communications channels and options into a single point of access. In fact, most UC products reply on VoIP as a core foundation, and many VoIP providers do offer some UC features in their portfolios to further extend the capabilities and flexibility.
Common UC features include:
- Unified Messaging
- Instant Messaging (chat)
- Presence
- Corporate Directory
- Video Conferencing
- Team Collaboration
3) Is it possible to integrate into other platforms and tools?
It’s critical for businesses to stay agile and ready in such a fast-changing world. With more and more systems, platforms, and software appearing in the workplace, both managers and employees expect to have a unified and integrated solution to improve efficiency, which is why a VoIP system’s ability to integrate and seamlessly work with other solutions becomes way more important than ever.
With your telephony system connected to other business-enhancing tools, it will be easier for you and your team to communicate, collaborate, engage with one another, and streamline the overall workflow. Fortunately, there are VoIP providers that ensure their phone service is compatible with some popular collaboration and communication tools.
VoIP Phone System Buyer’s Guide
When shopping for VoIP, you’ll find there is a list of providers competing for your attention. If you need more information to help figure out what kind of phone system is the best fit for your organization. Here is a Business Phone System Buyer Guide for you! This guide includes all the key information and useful tips to help you make an informed decision more easily. It will help you understand just how VoIP phone systems work, how to select a provider, and whether this is preferable to regular phone service. Just click to download!
If you wish to test a VoIP phone system to experience how it will work for your business in real business scenarios, we offer a 30-day free trial of Yeatar P-Series Phone System. It provides all-inclusive features of PBX, call center, omnichannel messaging (WhatsApp, SMS, etc), integrated video conferencing, and more big business features at small business prices.
History of VoIP
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) has revolutionized the way we communicate, transforming traditional telephony into a versatile, internet-based service. Its journey began in the mid-1990s, driven by the rapid expansion of the internet.
In 1995, the first VoIP service was introduced by VocalTech. This pioneering technology allowed users to make voice calls over the internet, marking the beginning of a new era in communication. However, early VoIP services faced several challenges, including call drops and distortions, which made for a poor user experience.
Despite these challenges, the technology continued to evolve and improve. By the early 2000s, the IP-based telephony services had become more reliable and feature-rich, offering benefits such as call recording, custom caller ID, and voicemail to email. Simultaneously, businesses started adopting VoIP for its cost savings and flexibility. Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) emerged as a standard protocol, facilitating the integration of internet-based phone service with existing phone systems and SIP-based devices like gateway, IP phones, etc.
Today, Voice over IP is an integral part of global communication, providing a cost-effective, reliable, and versatile alternative to traditional phone systems. As technology continues to advance, the technology is poised to further transform how we connect and communicate.
Technical VoIP Terminology
Voice over IP involves several protocols and standards that are used to ensure phone calls are completed successfully and heard in crystal-clear call quality.
| Terms | Use Case |
|---|---|
| G.711 | Used for high-quality audio transmission over high-bandwidth networks. |
| G.729 | Enables low-bandwidth networks to support VoIP applications with high compression. |
| T.38 | Used for reliable and high-quality fax transmission over IP networks. |
| H.248 | Enables media gateway control and management in Voice over IP networks. |
| H.323 | Used for multimedia communication over IP networks, including video conferencing and IP telehony. |
| SIP | Enables the establishment, management, and termination of VoIP calls. |
| UDP | Used for transmitting voice data packets, prioritizing speed over reliability. |
| TCP | Enables reliable transmission of voice data packets, prioritizing reliability over speed. |
| RTP | Used for transmitting audio and video data in real-time over IP networks. |
| SRTP | Enables secure and encrypted transmission of RTP data packets. |




Thanks for sharing this amazing article. Really helpful
Is a watsapp call voip
Yes, they also use VoIP technology.
If necessary, can a VOIP telephone number be moved and re-ported to a traditional mobile telephone.
Hi Alex,
Can you please elaborate on your request and submit a ticket here? Our technical team will reach you soon.
Hello I need a contact information of your distributor in Nigeria.where I can get a quotation using my local excahnge.
Thank you.
Hello Uplook,
I will have our sales contact you. Thank you.