 A SIP server, also known as a SIP Proxy, is an indispensable tool for businesses that use VoIP phones. We will discuss the basics of how a SIP server works and why it’s important to have one for any business that is looking for an IP PBX system or VoIP phone system.
A SIP server, also known as a SIP Proxy, is an indispensable tool for businesses that use VoIP phones. We will discuss the basics of how a SIP server works and why it’s important to have one for any business that is looking for an IP PBX system or VoIP phone system.
Table of Contents
- What is SIP? →
- VoIP vs. SIP →
- What is a SIP Server? →
- How Does a SIP Server Work? →
- Main Benefits of a SIP Server →
- SIP Servers Enhance Network Security →
- SIP Server vs. SIP Trunking? →
- SIP Server vs VoIP? →
- In Conclusion →
What is SIP (Session Initiation Protocol)?
SIP is a signaling protocol that establishes, configures, and terminates the sessions between two endpoints on a network. SIP was created to support voice and video calls from one endpoint to another by using IP networks. It can also be used for instant messaging, presence information, or file transfers.
RFC 2543 is a standard that defines the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP). It was published by the IETF (Internet Engineering Task Force) in 1999. It was developed to overcome the shortcomings of its predecessor H.323, which was limited by a reliance on centralized call routing information servers, and some aspects were not standardized at all. Other advantages over H.323 are that it can support video and audio calls. It offers more features than H.323. It provides a better-quality connection and supports both unicast and multicast transmissions. It offers a simpler design than H.323 due to the fewer functions required in each node.
RFC 2543 has been superseded by newer versions of the protocol but still remains relevant today because it provides a foundation on which other standards are built.
What is the Difference Between VoIP and SIP?
VoIP refers to the type of phone call that takes place over the Internet. VoIP relies on data connectivity to transmit voice packets rather than the public switched telephone network (PSTN).
SIP is the industry standard protocol that enables business VoIP communication between devices. Additionally, it also enables text and video so that your communications system can be more flexible and interact with other protocols. Many SIP trunking service providers may also offer VoIP and unified communications as a service (UCaaS).
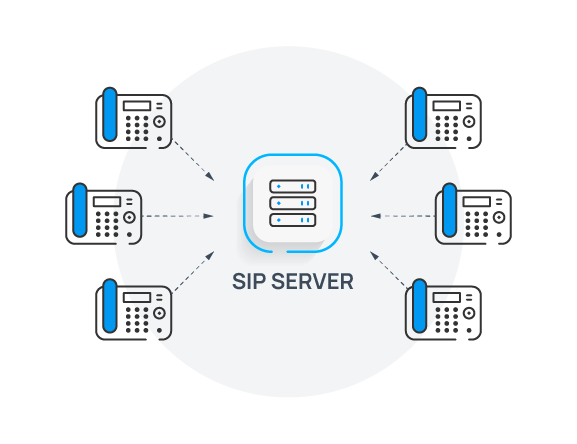
What is a SIP Server (SIP Proxy)?
The SIP server is an essential part of any PBX (Private Branch Exchange) system, handling the protocol and all SIP call routing in the network. These servers are designed to enable communication between two or more users using SIP, regardless of their location. SIP servers can be used to create, modify, or terminate telephone calls in response to requests from other types of devices on a network. It performs functions such as call signaling (e.g., dialing), call setup, and managing user authentication.
You can deploy a SIP proxy server in an organization’s internal network, or it can be hosted by a third-party carrier. The hardware can vary in size from something small like an old desktop PC to enterprise-level servers with multiple CPUs and hard drives. There are also cloud-based services that offer hosted VoIP solutions without requiring you to buy or maintain any physical equipment at your business location.
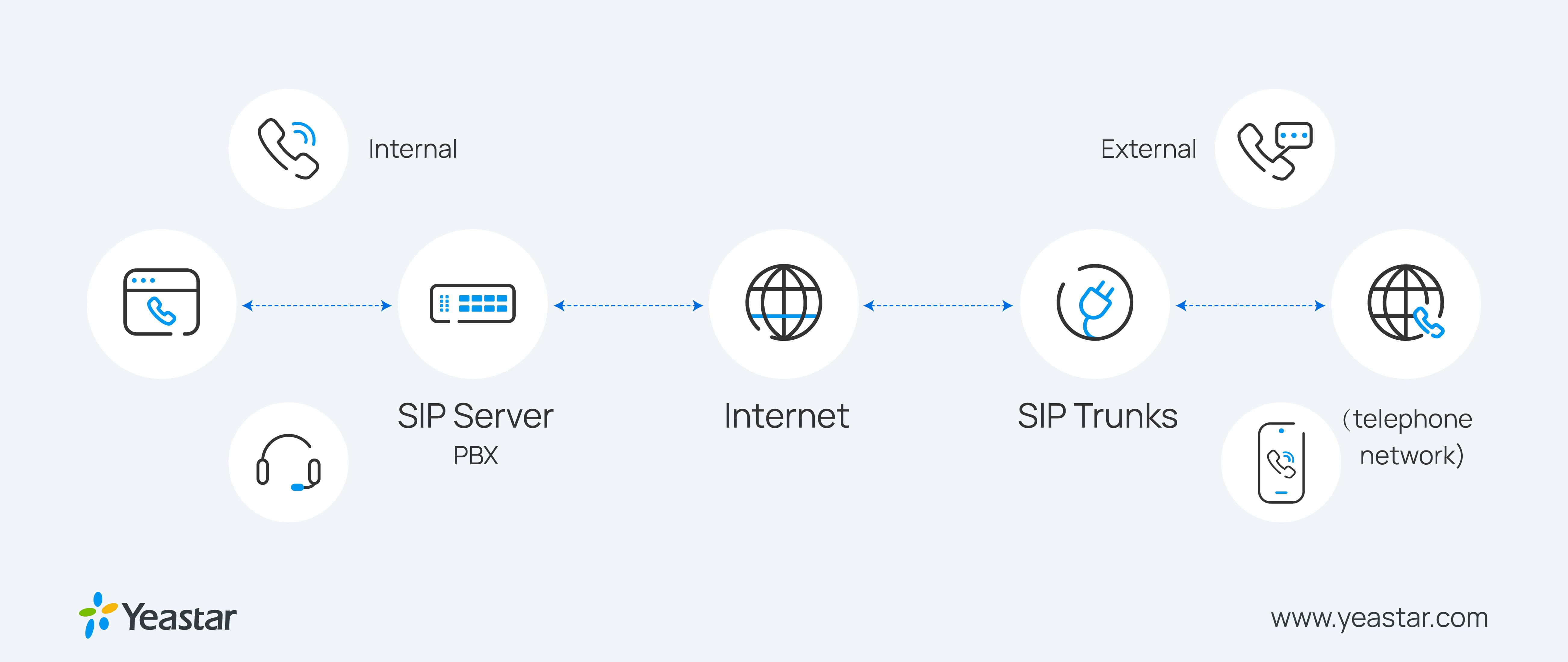
How Does a SIP Server Work?
Think of the SIP server as a “staging area”. It is responsible for the transmission and termination of calls via two types of servers. There are two types of SIP proxy servers: stateless and stateful. The main difference is that a stateless proxy server doesn’t save any information from the previous session, whereas a stateful proxy server does.
Stateless SIP Proxy Server
A stateless SIP Proxy is a proxy server that does not store any of the call information. This means that there are no records, which would typically be kept to troubleshoot and manage connections. Stateless proxies can function with less memory and CPU usage than stateful SIP proxies because they don’t need to store information on connections. They also benefit from being more scalable in terms of load balancing and having shorter response times for requests since there is no need to spend time processing the request before returning it.
Stateful SIP Proxy Server
While stateless proxies only route packets, a stateful SIP proxy stores all of the information related to each call. This way, if there are any problems with your connection, you can go back and look at the logs from your calls. Also, if one SIP user agent drops out, it can re-establish the connection with the other endpoint without having to initiate a new session. This saves bandwidth for both parties as well as time as there are no delays when setting up new connections.
The downside is that stateful SIP proxies have more overhead than stateless ones and are also more expensive because they need more resources to store data.
Main Benefits of a SIP Server
A sip server can provide many benefits, such as reducing bandwidth costs, improving call handling, increasing dialing efficiency, and providing better performance via load-balancing. SIP has lower latency than other protocols, meaning there is less lag time between when you speak and when your words are heard by the person on the other end of the line.
In addition, a business can benefit from lower costs due to fewer phone lines, greater mobility, more flexibility in using different devices for communications purposes, and increased security.
SIP Servers Enhance Network Security
A SIP server will secure your network by checking a user’s identity before they can send or receive any data packets. A SIP server is also required to use Message Digest Authentication.
Message Digest (MD) authentication provides a mechanism for verifying the identity of a peer before exchanging session keys. This is done by using HMAC-MD5 (Hash Message Authentication Code with MD5) as the algorithm, which uses a shared secret key to generate an encoded message digest that can be decoded only by the other party in possession of the same secret key. The main benefit of this protocol is its ability to provide integrity and authentication services without having to send passwords over unprotected channels or store them on each device.
What is the Difference Between a SIP Server and SIP Trunking?
Though both using SIP protocols, SIP server and SIP trunking are two different terms. SIP server is a network device that facilitates internet-based telephony for businesses, while SIP trunking is actually a telephony service that connects your company’s IP PBX to an Internet telephony service provider (ITSP).
Think of SIP trunking as a virtual version of analog phone lines. It is often used in enterprise environments to replace legacy PBX systems that were traditionally installed with each phone on its own dedicated line. With SIP trunking, the calls are routed via your internet service provider rather than being carried by traditional PSTN lines.
What is the Difference Between a SIP Server and VoIP Server?
The primary difference between a SIP server and a VoIP server lies in their specific roles within the communication framework. A SIP server, which operates using the Session Initiation Protocol, is primarily responsible for managing the signaling involved in setting up, modifying, and terminating multimedia sessions, such as voice and video calls. It handles tasks like user registration, call routing, and session management, acting as an intermediary that facilitates communication between endpoints (user devices) and other servers within the network.
In contrast, a VoIP server encompasses a broader range of functionalities related to Voice over Internet Protocol technology. While it may utilize SIP for signaling, a VoIP server also manages the actual transmission of voice data over the internet, often integrating various protocols to handle media streams. Essentially, all SIP servers can be considered VoIP servers due to their role in voice communication; however, not all VoIP servers are SIP servers, as they may support additional protocols and features beyond SIP
In Conclusion
SIP is a very important technology that has a number of different purposes. In general, SIP is most often used with VoIP to set up and manage a call. A SIP server has many uses, such as video conferencing, instant messaging, call forwarding, and other types of call and video services.
We hope you found this article useful and now understand how a SIP server works and its benefits.


We are looking for SIP Based IPPBX for total 1300 users to work with Copper or GPoN based OLT and ONT and SIP based IP Video Door Phone System scalable to 2500 users Extensions for future phase The SIP Server Must have 1300 Video License with Concurrency of 300 Calls. We are basically system integrators. Please Let me know how can we work together.
Hello Sandeep,
Our sales rep has reached you for more details.
I am in fact thankful to the holder of this site who has shared this fantastic piece
of writing at here.
Thanks.