 Communication is key. This age-old adage is one of the driving forces behind most of the technological progress we’re experiencing nowadays. From ultra-high-speed internet connections to new devices that let us get in touch with each other in ways that were previously unimaginable.
Communication is key. This age-old adage is one of the driving forces behind most of the technological progress we’re experiencing nowadays. From ultra-high-speed internet connections to new devices that let us get in touch with each other in ways that were previously unimaginable.
Telephony, from traditional phone systems all the way to the cloud-hosted phone networks of the 21st century, has always been at the center of the communication revolution. It is especially important in the world of business, where offices make hundreds, if not thousands of calls, every single day, both externally and internally.
From traditional Private Branch Exchange (PBX) systems to the introduction of Voice over IP (VoIP) technology, to the rapid development of Unified Communications (UC), the way we understand telephony in an office environment has changed dramatically in just a few decades.
The development of broadband Internet connection has brought significant changes to the world of office phone solutions, with the introduction of Internet protocol telephony (IP telephony). IP telephony offers cheaper running costs and more advanced business phone features. It has made traditional phone solutions all but redundant and established a new quality standard in the industry. If you want to know more about how it works and the potential benefits of IP telephony for your business, read on.
Table of Contents
- What is IP Telephony and How Does It Work? →
- IP Telephony vs. VoIP →
- IP Telephony vs. Other Telephony Solutions →
- Benefits of Using IP Telephony →
- What You Need to Get Started with IP Telephony →
- Key Components of IP Phone Systems →
- Different Types of IP Phone Systems →
- Yeastar IP Telephony Solutions →
What is IP Telephony and How Does It Work?
IP telephony is a phone system made possible thanks to VoIP (Voice Over Internet Protocol) technology. It’s also sometimes referred to as an IP phone system, IP PBX, or a VoIP phone system. IP telephony enables users to carry out and receive phone calls via a simple internet connection, as opposed to the legacy landline systems, which made use of long, tangle-prone cables that were often difficult to install.
Legacy phone systems carry voice through landline cables by directly transmitting your analog voice signals and carrying them through to the addressee. VoIP, on the other hand, converts your analog signals into digital signals, or data packages, which are then sent through your broadband connection to the receiver.
These converted bits of data are known as packet-switched protocols. You can think of them as tiny, digital envelopes. In real-time, your voice is sliced apart, packaged into these “envelopes”, instantly sent to the addressee, and unpackaged so that they get the message. IP telephony calls can be transmitted via a regular internet connection, as well as a local area network (LAN).
Due to the fact that VoIP telephony makes use of the internet connection at your office to transmit voice signals across devices, before installing it, you’re going to need to make sure that your company’s broadband is up to the task, and that your office is equipped with SIP endpoints like IP phones or VoIP gateways to support your analog phones. Without the broadband connection and the right devices, IP telephony at your company will be all but impossible.
IP Telephony vs. VoIP
IP Telephony is a broader term that encompasses the full set of technologies, products, and services that use the Internet Protocol (IP) to support various forms of communication, including voice calling, voicemail, video calling, video conferencing, faxing, and instant messaging (IM). It refers to the entire suite of features that can be provided over an IP network, which includes both voice and non-voice services.
VoIP, on the other hand, is a more specific term that describes the technologies used to deliver voice-based features over IP networks. It is essentially a subset of IP telephony that focuses on voice communication services. VoIP involves converting analog voice signals into digital data packets that are transmitted over the internet.
To summarize, VoIP is a specific technology encompassed by IP telephony. IP telephony, on the other hand, represents a broader approach to communication that encompasses various services beyond VoIP.
IP Telephony vs. Other Telephony Solutions
Of course, IP telephony is not the first (and probably not the last) communications solution that ever existed in offices all around the world. Traditionally, office telephony was done through the POTS (Plain Old Telephone System) method. Every single phone in the office needed its own separate phone line connecting it to the service provider, as well as its own, unique phone number. As you can imagine, it caused a lot of confusion and was very inconvenient. After all, dialing a lengthy number when you’re in a hurry does not necessarily scream “efficiency”.
The first improvement upon POTS in offices was Private Branch Exchange systems, which allowed for call routing to different phones in the office via switchboard operators. They were human employees, who manually received each call and passed it on to the addressee by pressing buttons and re-plugging cables on the switchboard. It increased the efficiency of call-making in the office, and in time, it became the most frequently used communication system for the majority of large enterprises. Smaller businesses could also implement PBX for their business phone needs, but it often entailed having to enlist the services of a shared operator center, significantly slowing down the connection times.
This issue was resolved by the arrival of Private Automatic Branch Exchange (PABX) services, which worked in a very similar manner to its predecessor, except for the fact that it completely eradicated the need for the middleman, or operator, to transfer the calls. It was made possible by the creation of devices with buttons allowing for a wide range of call-transferring options. All of the phones in one office were connected to one network, and to get in touch with a co-worker, all one had to do was dial their extension number, which was usually only one or two digits. PABX systems continue to be used by businesses around the world to this day, and the advent of IP-based telephony only made these solutions more efficient.
IP telephones are devices capable of connecting to the Internet and taking advantage of the possibility of carrying out voice communications via Internet protocol. This has led to major improvements in call quality, decreased the influence of over-priced landline providers on the communications industry, and allowed for the implementation of plenty of additional features, alongside the basic phone calls.
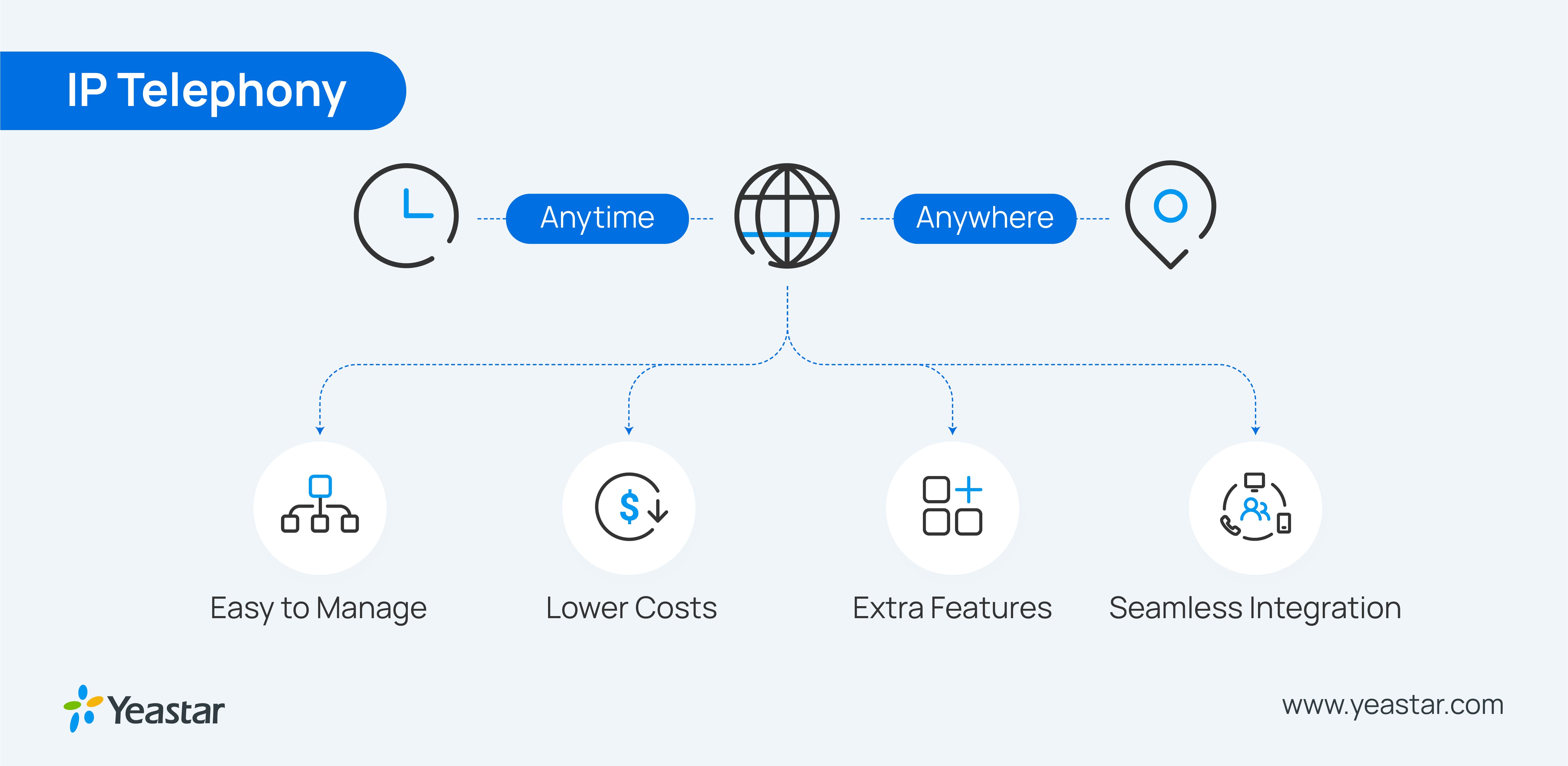
Benefits of Using IP Telephony
Using IP telephony services can be incredibly beneficial for your business, regardless of its scale and the industry you work in. If you work for a major corporation, VoIP technology will allow you to seamlessly connect to the firm’s other branches all around the world. As for start-ups and small businesses, these establishments can benefit greatly from the money saved by making the switch from a landline-based PBX to IP phones.
Cost-effectiveness
This is probably the most frequently cited reason why CEOs and office managers make the switch to IP telephony systems. It’s simple: if there is an opportunity to save money, most businesses will take it. While changing to IP telephony requires providing each desk at the office with an IP phone, it is possible to implement this system even without such devices, given that most VoIP service providers also offer softphones that can be installed on smartphones and computers.
Regardless of how you choose to go about the device issue, the bottom line is that changing to an IP telephone system will save you hundreds, if not thousands of dollars annually when compared to landline-based business solutions.
Less Clutter Around the Office
Legacy telephone systems tend to require their users to accumulate a whole load of cables all over the office. It is one of the biggest drawbacks of traditional phone lines. It’s also one of the shortcomings that IP telephony has set out to fix. With an internet-based phone system, all you’ll ever need to make phone calls is a working internet connection.
More Extra Features
IP telephony not only fulfills all the functions of POTS (Plain Old Telephone System) without the loss of sound quality but also opens up plenty of possibilities for additional functions, including presence, video conferencing, instant messaging, etc. are all going to be within your reach with IP telephony.
Seamless Integration with Business Tools
One of the biggest doubts managers have when considering switching to IP-based phone systems is whether or not they will be able to integrate their new IP-based communication system with other business tools. Thankfully, doing so is even easier than in the case of landlines. Taking your phone system into the digital sphere means that all of the integration can be done almost instantly, with the help of your IT team. No need to bring in outside experts to install complicated equipment!
What You Need to Get Started with IP Telephony
The best thing about VoIP is the fact that to get started with it, you don’t really need anything except a working broadband connection and devices capable of connecting to the internet. Of course, buying actual IP phones for your office is preferable, but it can be done later on in the process. If you’re in a hurry to get the system up and running, all you’re going to need is a working internet connection and devices capable of going online, such as computers or smartphones.
Key Components of IP Phone Systems
IP phone systems are composed of several key components that work together to facilitate voice communications over IP networks. These components include:
- IP PBX: Acts as the central hub for call routing and management.
- IP Phones: Convert voice into digital data for network transmission.
- Softphones: Software applications that allow for phone calls using a computer or mobile devices.
- VoIP Gateways: Connect IP systems to traditional phone lines.
- Session Border Controllers (SBCs): Secure the IP telephony network and manage traffic.
- Network Infrastructure: High-speed internet and proper setup to support voice data.
Different Types of IP Phone Systems
On-premises IP Phone System
This system is installed and maintained at the business’s location. It offers businesses more control over their telephony infrastructure but requires on-site maintenance and can have higher initial costs.
Hosted VoIP(Cloud PBX)
With a hosted IP PBX, the service provider manages the IP PBX in the cloud. Businesses typically pay a monthly fee, which often includes maintenance and support. This option is often more cost-effective for small to medium-sized companies and offers scalability.
Yeastar IP Telephony Solutions
When choosing Yeastar as your unified communications provider, you’re going to gain access to a whole host of great features on top of your regular PBX phone service. These include call center capabilities, video conferencing, instant messaging, presence, call recording, CRM integration, and many more. Most of these features are accessible through Linkus UC Clients, available on web browsers, mobile phones, as well as Windows, and Mac OS.
With Yeastar, you’re also going to be able to choose between a cloud-hosted service or on-premises equipment to gain total control over your office’s communications. Both of them will grant your company more freedom and flexibility in handling your communications. Want to learn more about your options and what Yeastar has to offer? Here is an evaluation guide that includes product and solution descriptions, case studies, partner programs, training, etc. Click below to download!

